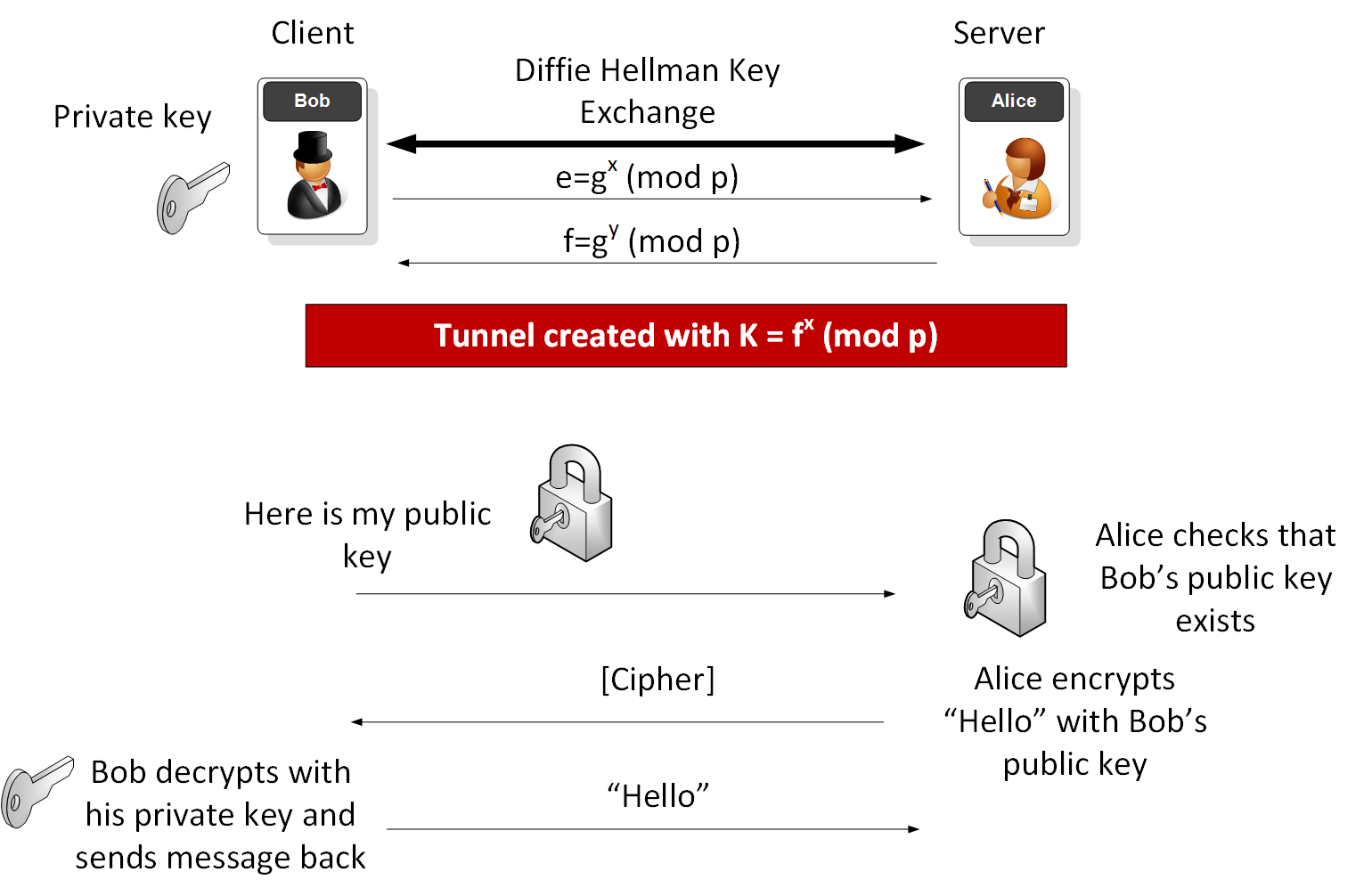
Ssh Sha256
Firstly SHA, AES and RSA are three different types of encryption. Let us check them 1 by 1. RSA:- It is an asymmetric cryptography, i.e. It uses a key to encrypt data and then uses a different key for decryption. These are normally called a public.
In Windows you can make a checksum of a file without installing any additional software.
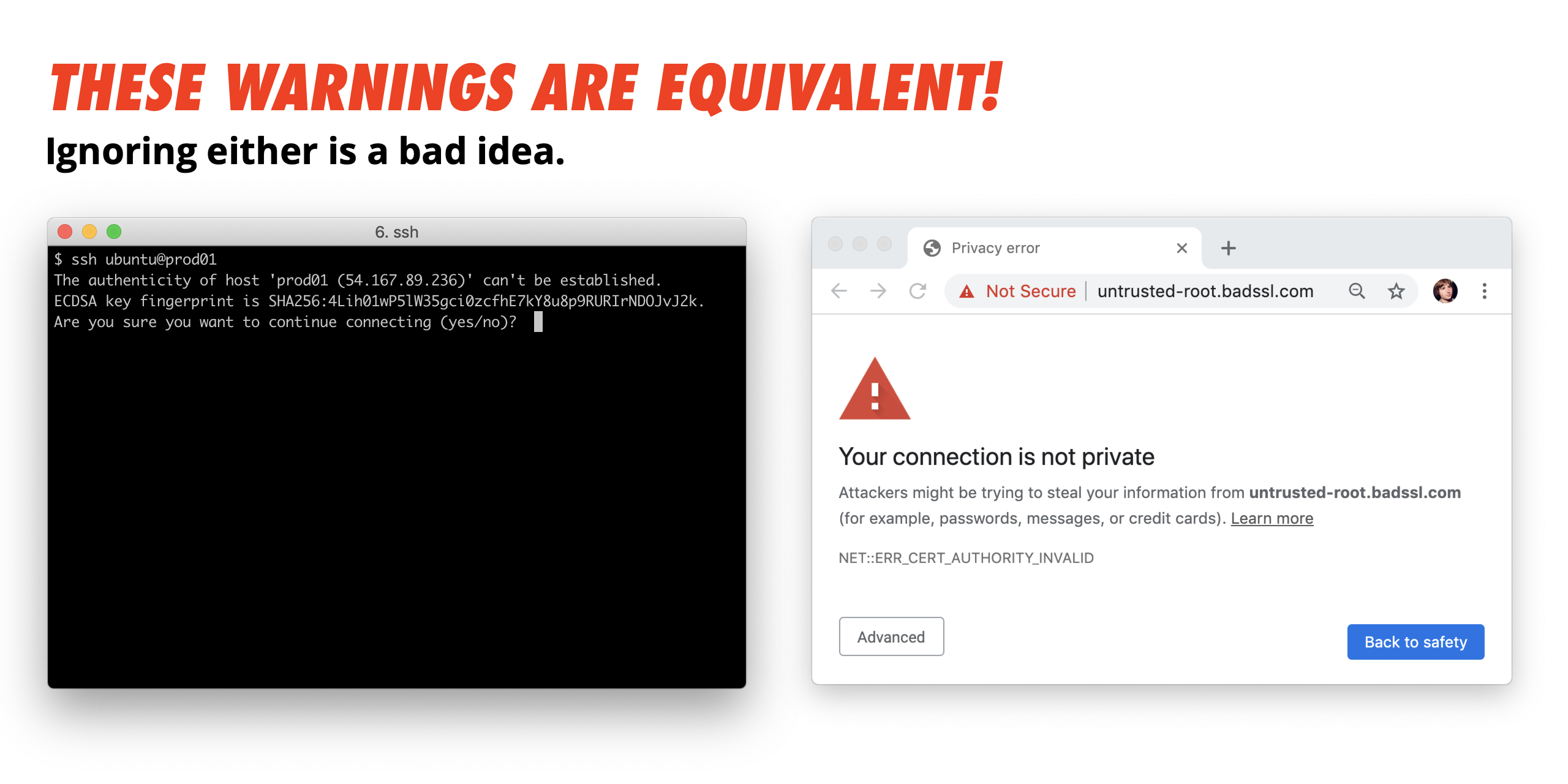
- How to SSH Properly Jan 25, 2021 by Gus Luxton This blog post has been updated as of. SSH Best Practices. There’s no denying that SSH is the de facto tool for *nix server administration.
- Add the following lines to my /etc/ssh/sshconfig. KexAlgorithms diffie-hellman-group1-sha1,curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1 Ciphers 3des-cbc,blowfish-cbc,aes128-cbc,aes128-ctr,aes256-ctr regenerate keys with.
For this you can use the certUtil – built-in command-line utility that works both in Windows CMD and Powershell.
In this note i will show the examples of how to make md5sum and sha256sum of a file in Windows from the command line.
Cool Tip:zip and unzip from the command line in Windows! Read more →


MD5/SHA256 CheckSum in Windows
Checksum a file in Windows using the built-in certUtil command-line utility:
MD5 checksum example (md5sum):
SHA256 checksum example (sha256sum):
Get only hash value:
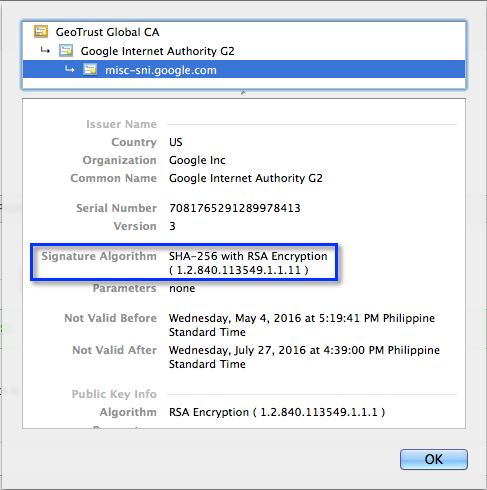
Available hash algorithms:
Hash Algorithms: Note that on Windows 7, the hash algorithms are case-sensitive. Be sure to type, for example, not “md5” but “MD5”. In the subsequent versions of Windows the case doesn’t matter.
Get help:
The Secure Hash Algorithms are a family of cryptographic hash functions published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as a U.S.Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS), including:
- SHA-0: A retronym applied to the original version of the 160-bit hash function published in 1993 under the name 'SHA'. It was withdrawn shortly after publication due to an undisclosed 'significant flaw' and replaced by the slightly revised version SHA-1.
- SHA-1: A 160-bit hash function which resembles the earlier MD5 algorithm. This was designed by the National Security Agency (NSA) to be part of the Digital Signature Algorithm. Cryptographic weaknesses were discovered in SHA-1, and the standard was no longer approved for most cryptographic uses after 2010.
- SHA-2: A family of two similar hash functions, with different block sizes, known as SHA-256 and SHA-512. They differ in the word size; SHA-256 uses 32-byte words where SHA-512 uses 64-byte words. There are also truncated versions of each standard, known as SHA-224, SHA-384, SHA-512/224 and SHA-512/256. These were also designed by the NSA.
- SHA-3: A hash function formerly called Keccak, chosen in 2012 after a public competition among non-NSA designers. It supports the same hash lengths as SHA-2, and its internal structure differs significantly from the rest of the SHA family.
The corresponding standards are FIPS PUB 180 (original SHA), FIPS PUB 180-1 (SHA-1), FIPS PUB 180-2 (SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512). NIST has updated Draft FIPS Publication 202, SHA-3 Standard separate from the Secure Hash Standard (SHS).
Comparison of SHA functions[edit]
Ssh Sha256
In the table below, internal state means the 'internal hash sum' after each compression of a data block.
| Algorithm and variant | Output size (bits) | Internal state size (bits) | Block size (bits) | Rounds | Operations | Security against collision attacks (bits) | Security against length extension attacks (bits) | Performance on Skylake (median cpb)[1] | First published | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long messages | 8 bytes | ||||||||||
| MD5 (as reference) | 128 | 128 (4 × 32) | 512 | 64 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or | ≤ 18 (collisions found)[2] | 0 | 4.99 | 55.00 | 1992 | |
| SHA-0 | 160 | 160 (5 × 32) | 512 | 80 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or | < 34 (collisions found) | 0 | ≈ SHA-1 | ≈ SHA-1 | 1993 | |
| SHA-1 | < 63 (collisions found)[3] | 3.47 | 52.00 | 1995 | |||||||
| SHA-2 | SHA-224 SHA-256 | 224 256 | 256 (8 × 32) | 512 | 64 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or, Shr | 112 128 | 32 0 | 7.62 7.63 | 84.50 85.25 | 2004 2001 |
| SHA-384 SHA-512 | 384 512 | 512 (8 × 64) | 1024 | 80 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 264), Or, Shr | 192 256 | 128 (≤ 384) 0[4] | 5.12 5.06 | 135.75 135.50 | 2001 | |
| SHA-512/224 SHA-512/256 | 224 256 | 112 128 | 288 256 | ≈ SHA-384 | ≈ SHA-384 | 2012 | |||||
| SHA-3 | SHA3-224 SHA3-256 SHA3-384 SHA3-512 | 224 256 384 512 | 1600 (5 × 5 × 64) | 1152 1088 832 576 | 24[5] | And, Xor, Rot, Not | 112 128 192 256 | 448 512 768 1024 | 8.12 8.59 11.06 15.88 | 154.25 155.50 164.00 164.00 | 2015 |
| SHAKE128 SHAKE256 | d (arbitrary) d (arbitrary) | 1344 1088 | min(d/2, 128) min(d/2, 256) | 256 512 | 7.08 8.59 | 155.25 155.50 | |||||
Ssh Curve25519-sha256
Validation[edit]
All SHA-family algorithms, as FIPS-approved security functions, are subject to official validation by the CMVP (Cryptographic Module Validation Program), a joint program run by the American National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Canadian Communications Security Establishment (CSE).
Cisco Ssh Sha256
References[edit]
Ssh-keygen Sha256 Format
- ^'Measurements table'. bench.cr.yp.to.
- ^Tao, Xie; Liu, Fanbao; Feng, Dengguo (2013). Fast Collision Attack on MD5(PDF). Cryptology ePrint Archive (Technical report). IACR.
- ^Stevens, Marc; Bursztein, Elie; Karpman, Pierre; Albertini, Ange; Markov, Yarik. The first collision for full SHA-1(PDF) (Technical report). Google Research. Lay summary – Google Security Blog (February 23, 2017).
- ^Without truncation, the full internal state of the hash function is known, regardless of collision resistance. If the output is truncated, the removed part of the state must be searched for and found before the hash function can be resumed, allowing the attack to proceed.
- ^'The Keccak sponge function family'. Retrieved 2016-01-27.