Normal Pulse Of Human Body
Have you ever wondered what pulse rate actually stands for? Do you know what the normal pulse rate is? And how to measure it? Today we get to talk about one very significant topic that refers to our heart health and how we can enhance it. Let’s see what your pulse rate is telling you!
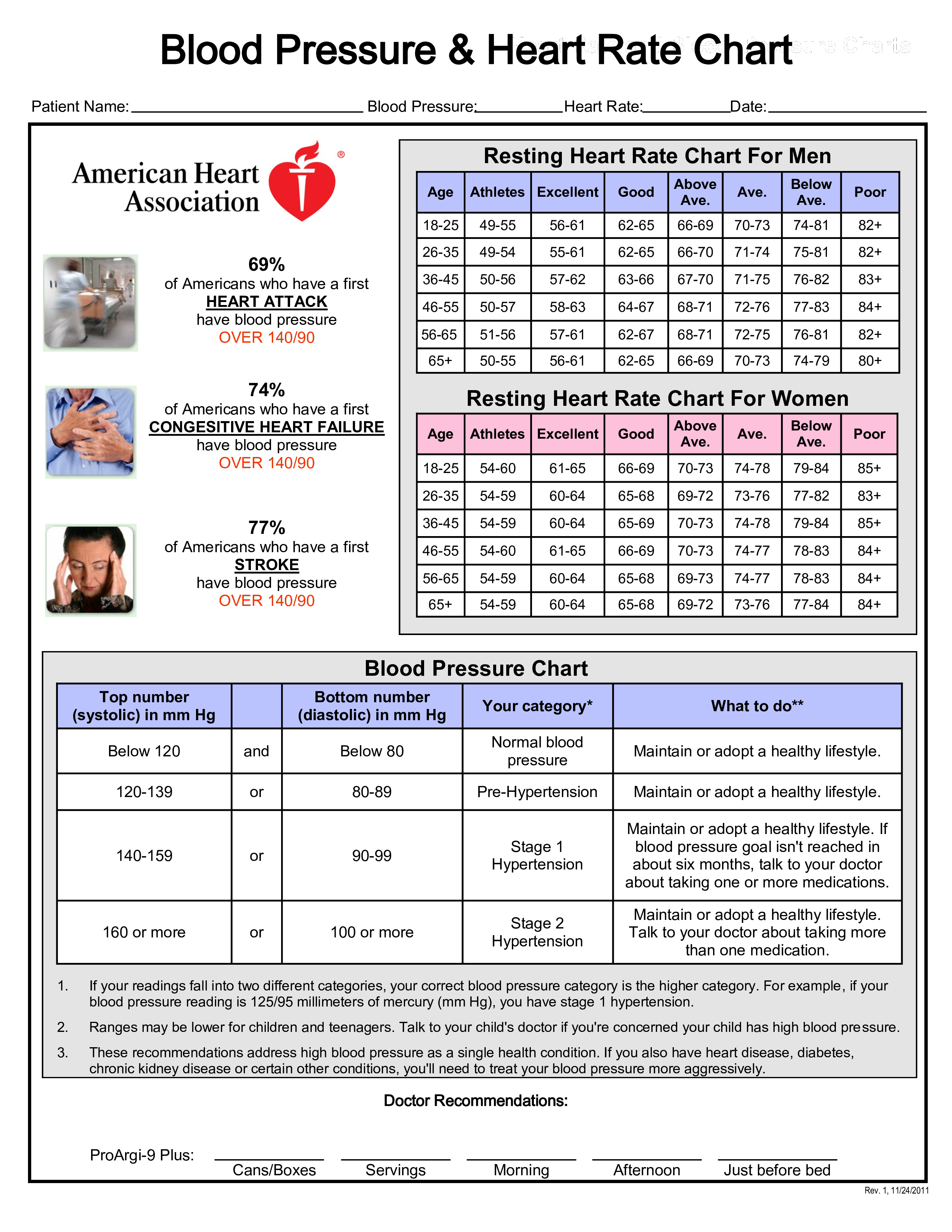
A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. Generally, a lower heart rate at rest implies more efficient heart function and better cardiovascular fitness. For example, a well-trained athlete might have a normal resting heart rate closer to 40 beats per minute. To measure your heart rate, simply check your pulse. Your pulse rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate should be 60–100 beats per minute, but it can vary from minute to minute. It can go up to 130–150 beats or higher per minute when you’re exercising – that’s normal because the body needs to pump more oxygen-rich blood around the body. What is a normal heart rate? A normal heart rate, when you're not being active, is between 60 – 100 beats per minute. This is called your resting heart rate. If you've been active, you'll need to wait at least five minutes before taking your pulse.
What Is Pulse Rate?
Pulse rate refers to the number of times that the arteries expand and contract in one minute as a response to the heart pumping blood. A lot of people mistaken the pulse rate for heart rate. Heart rate is the number of times that the heartbeats in one minute. So when we are talking about pulse rate, we are talking about arteries, and when we are talking about heart rate, we are talking about the heart itself. Perhaps the reason why these two are often mistaken is the fact that the pulse rate is equal to the heartbeat. When the heart contracts, it causes an increase in blood pressure in the arteries, which leads to a pulse to be registered. The pulse rate is used as a direct measure of the heart rate.
Pulse rate is easily measured, and everyone can do it. All that you have to do is to place the tips of the index, second, and the third finger on the palm side of the wrist, on the other hand, somewhere below the base of the thumb. You can search until you feel a strong pulse, which is where you can measure your pulse rate. Count the beats for 10 seconds. The number that you are going to get is to be multiplied by 6. This is your pulse rate. Another way to measure your pulse rate is to do the same procedure, but instead of placing your fingers on your wrist, you can place them on your lower neck on either side of the windpipe.
Normal Human Pulse
Resting Pulse Rate vs. Maximum Pulse Rate
There is a difference between your resting and your maximum pulse rate. When you are resting, your heart pumps the lowest amount of blood as a way to supply the whole body with the much-needed blood. This is when a resting pulse rate is to be measured. When you are sitting still, lying down, and being relaxed and calm, resting pulse rate is present. On the other hand, the maximum pulse rate is when the heart is working the hardest in order to supply your body with blood. This happens whenever you are being physically active, especially when you are doing a heavy workout, running, etc.
What Is The Normal Pulse Rate For Adults?
For adults, the normal pulse rate is considered to be around 60 beats per minute. This is usually their resting pulse rate. Their pulse rate can go as high as 100 if the individual is using certain medications, has a fever, anemia, etc. If the resting pulse rate is constantly at 100 beats per minute, a doctor needs to be consulted as soon as possible. The maximum pulse rate can be around 150 to 180 beats per minute, depending on the age of the individual.
What Is A Good Pulse Rate For Women?
The normal pulse rate for women should be 60 to 100 beats per minute. A good pulse rate, however, is considered to be around 60 to 70 beats per minute. A pulse rate that is constantly above 80 needs to be discussed with a doctor. A high pulse rate can indicate an increased risk of a heart attack.
What Is A Good Pulse Rate For Men?
For men, the same values apply to women. Men are more likely to have a pulse rate of 60 beats per minute. In addition, for many professional athletes, a pulse rate of around 40 beats per minute is also considered to be normal.
What Is The Normal Pulse Rate For Children?
For children aged 6 to 15, the normal resting pulse rate is around 70 to 100 beats per minute. Babies have the highest pulse rate, with around 180 beats per minute. The pulse rate slows down with their age until it reaches the limit of the normal pulse rate of an adult.
Normal Pulse Rate By Age – Infants & Children
| Age | Pulse Rate |
|---|---|
| < 1 year | 110 – 160 |
| 1 – 2 year | 100 – 150 |
| 2 – 5 year | 95 – 140 |
| 5 – 12 year | 80 – 120 |
| > 12 year | 60 – 100 |
How To Lower Pulse Rate Naturally?
In order to lower your high pulse rate, you need to practice mindful breathing. It is an effective technique that will help you to lower your high pulse rate at moments when you feel anxious or stressed. Exercising is also a great way to combat a high pulse rate. Smoking and a sedentary lifestyle seem to have the greatest negative effects on one’s pulse rate. Make sure to eat more fish since fish is the biggest source of the much needed Omega-3 fatty acids that are essential for your heart health.
Conclusion
A normal pulse rate is easily measured using just your fingers. It takes a couple of seconds, and it reveals so much more information about your heart health. Create a habit for yourself where you track your normal pulse rate and consult your doctor when you notice that your pulse rate is constantly elevated.
Doctor, author and fitness enthusiast, Ahmed Zayed, MD, is a surgery resident with a passion for helping people live a happy healthy life. He is the author of numerous health-related books and contributor to several medicine, health and wellbeing websites.
Overview
What is your pulse?
Your pulse is your heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one minute. Pulse rates vary from person to person. Your pulse is lower when you are at rest and increases when you exercise (more oxygen-rich blood is needed by the body when you exercise). Knowing how to take your pulse can help you evaluate your exercise program.
How to take your pulse
- Place the tips of your index, second and third fingers on the palm side of your other wrist below the base of the thumb. Or, place the tips of your index and second fingers on your lower neck on either side of your windpipe.
- Press lightly with your fingers until you feel the blood pulsing beneath your fingers. You may need to move your fingers around slightly up or down until you feel the pulsing.
- Use a watch with a second hand, or look at a clock with a second hand.
- Count the beats you feel for 10 seconds. Multiply this number by six to get your heart rate (pulse) per minute.
Count your pulse: _____ beats in 10 seconds x 6 = _____ beats/minute
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-normal-respiratory-rate-2248932-v1-5c1abe6846e0fb0001c6284a.png)
What is a normal pulse?
Normal heart rates at rest:
- Children (ages 6 - 15) 70 – 100 beats per minute
- Adults (age 18 and over) 60 – 100 beats per minute
Test Details
What is maximum heart rate?
The maximum heart rate is the highest heart rate achieved during maximal exercise. One simple method to calculate your predicted maximum heart rate, uses this formula:
220 - your age = predicted maximum heart rate
Example: a 40-year-old's predicted maximum heart rate is 180 beats/minute.
There are other formulas that take into account the variations in maximal heart rate with age and gender. If you are interested in learning more about these more accurate but slightly more complicated formulas please see these resources:
Normal Pulse Rate Of Human Body Per Minute
- Gellish RL, Goslin BR, Olson RE, McDonald A, Russi GD, Moudgil VK. Longitudinal modeling of the relationship between age and maximal heart rate. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007 May;39(5):822-9. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17468581
- Gulati M, Shaw LJ, Thisted RA, Black HR, Bairey Merz CN, Arnsdorf MF. Heart rate response to exercise stress testing in asymptomatic women: the st. James women take heart project. Circulation. 2010 Jul 13;122(2):130-7. Epub 2010 Jun 28. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20585008
Your actual maximum heart rate is most accurately determined by a medically supervised maximal graded exercise test.
Please note that some medications and medical conditions may affect your heart rate. If you are taking medications or have a medical condition (such as heart disease, high blood pressure or diabetes), always ask your doctor if your maximum heart rate/target heart rate will be affected. If so, your heart rate ranges for exercise should be prescribed by your doctor or an exercise specialist.
What is target heart rate?
- You gain the most benefits and lessen the risks when you exercise in your target heart rate zone. Usually this is when your exercise heart rate (pulse) is 60 to 80% of your maximum heart rate. In some cases, your health care provider may decrease your target heart rate zone to begin with 50% .
- In some cases, High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) may be beneficial. This should be discussed with a healthcare professional before beginning. With HIIT exercise, heart rates zones may exceed 85%.
- Always check with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program. Your provider can help you find a program and target heart rate zone that matches your needs, goals and physical condition.
- When beginning an exercise program, you may need to gradually build up to a level that's within your target heart rate zone, especially if you haven't exercised regularly before. If the exercise feels too hard, slow down. You will reduce your risk of injury and enjoy the exercise more if you don't try to over-do it!
- To find out if you are exercising in your target zone (between 60 and 80% of your maximum heart rate), stop exercising and check your 10-second pulse. If your pulse is below your target zone (see below), increase your rate of exercise. If your pulse is above your target zone, decrease your rate of exercise.
What is your target zone?
Target Heart Rate Zones by Age *
- Age: 20
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): ** 120 – 170
- Predicted Maximum HR: 200
- Age: 25
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 117 – 166
- Predicted Maximum HR: 195
- Age: 30
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 114 – 162
- Predicted Maximum HR: 190
- Age:35
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): ** 111 – 157
- Predicted Maximum HR: 185
- Age: 40
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 108 – 153
- Predicted Maximum HR: 180
- Age: 45
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 105 – 149
- Predicted Maximum HR: 175
- Age: 50
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 102 – 145
- Predicted Maximum HR: 170
- Age:55
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 99 – 140
- Predicted Maximum HR: 165
- Age:60
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 96 – 136
- Predicted Maximum HR: 160
- Age:65
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 93 – 132
- Predicted Maximum HR: 155
- Age:70
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 90 – 123
- Predicted Maximum HR: 150
Your Actual Values (Actual Values are determined from a graded exercise test)
Pulses In Human Body
- Target HR
- Max. HR
* This chart is based on the formula: 220 - your age = predicted maximum heart rate.
Resources
For more information about exercise
- Exercise for Your Heart Health.
- Exercise: Make Your Program a Success.
- To make an appointment with an exercise specialist or to join a cardiac rehabilitation program, contact the Cleveland Clinic Preventive Cardiology and Rehabilitation Program at 216.444.9353 or 800.223.2273, ext. 9353
- To find a cardiac rehabilitation program in your area, contact the American Association of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation.
- American Heart Association.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
