Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal
Scroll and find 'Run Code Configuration' Scroll and find a checkbox Run in Terminal (Whether to run code in Integrated Terminal) Check the box. In your setting.json file, add: 'code-runner.runInTerminal': true Hurray, you're done and ready to roll:). Here are some C resources you can use to get started with learning C.
- Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal To Usb
- Visual Studio Code Download
- Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal Command
- Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal File
- Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal Command
Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal To Usb
If you day to day life revolves around MacOS and Visual Studio Code but the rest of your team is working on Windows, you might see that many of them are using PowerShell.
- Download Visual Studio Code for Mac. Double-click on the downloaded archive to expand the contents. Drag Visual Studio Code.app to the Applications folder, making it available in the Launchpad. Add VS Code to your Dock by right-clicking on the icon and choosing Options, Keep in Dock.
- Drag Visual Studio Code.app to the Applications folder, making it available in the macOS Launchpad. Add VS Code to your Dock by right-clicking on the icon to bring up the context menu and choosing Options, Keep in Dock. Launching from the command line # You can also run VS Code from the terminal by typing 'code' after adding it to the path.
- This Video will help you to set the path to your Visual Studio Code to make it accessible from the bash terminal using command(code.) Leave a like if the vi.
You don’t have to be the odd-person-out, and besides that, PowerShell is an amazing shell in general, providing a scripting environment that is very hard to beat by other shells.
So, a few things to do:
Install PowerShell

Navigate to https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/blob/master/docs/installation/macos.md and follow the instructions. It’s pretty straightforward.Make sure that PowerShell works by launching a terminal and enter pwsh. If all goes okay you should see something alike.
Install Visual Studio Code
Of course, if you have Visual Studio Code installed already you can skip this step.
Again, a few simple steps (https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/setup/mac):
- Download Visual Studio Code for Mac.
- Double-click on the downloaded archive to expand the contents.
- Drag Visual Studio Code.app to the Applications folder, making it available in the Launchpad.
- Add VS Code to your Dock by right-clicking on the icon and choosing Options, Keep in Dock.
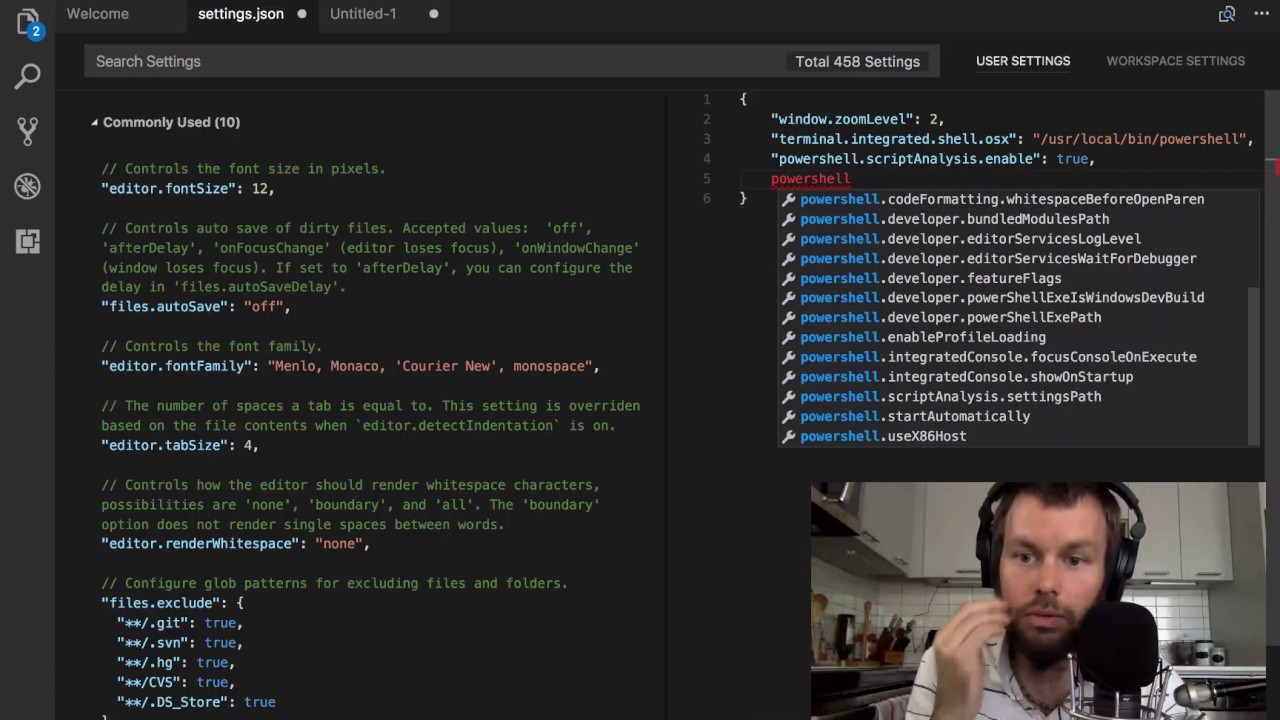
##Configure the terminal in Visual Studio CodeOpen Visual Studio Code, and modify the settings (⌘,)In the right pane (the user settings), add the following two lines:
Save your settings.
Visual Studio Code Download
Done!
Now if you open the integrated terminal in MacOS you will be greeted by a friendly PowerShell prompt.
-->This tutorial shows how to publish a console app so that other users can run it. Publishing creates the set of files that are needed to run an application. To deploy the files, copy them to the target machine.
The .NET CLI is used to publish the app, so you can follow this tutorial with a code editor other than Visual Studio Code if you prefer.
Prerequisites
- This tutorial works with the console app that you create in Create a .NET console application using Visual Studio Code.
Publish the app
Start Visual Studio Code.
Open the HelloWorld project folder that you created in Create a .NET console application using Visual Studio Code.
Choose View > Terminal from the main menu.
The terminal opens in the HelloWorld folder.
Run the following command:
The default build configuration is Debug, so this command specifies the Release build configuration. The output from the Release build configuration has minimal symbolic debug information and is fully optimized.
The command output is similar to the following example:
Inspect the files
By default, the publishing process creates a framework-dependent deployment, which is a type of deployment where the published application runs on a machine that has the .NET runtime installed. To run the published app you can use the executable file or run the dotnet HelloWorld.dll command from a command prompt.
In the following steps, you'll look at the files created by the publish process.
Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal Command
Select the Explorer in the left navigation bar.
Expand bin/Release/net5.0/publish.
As the image shows, the published output includes the following files:
HelloWorld.deps.json
This is the application's runtime dependencies file. It defines the .NET components and the libraries (including the dynamic link library that contains your application) needed to run the app. For more information, see Runtime configuration files.
HelloWorld.dll
This is the framework-dependent deployment version of the application. To execute this dynamic link library, enter
dotnet HelloWorld.dllat a command prompt. This method of running the app works on any platform that has the .NET runtime installed.HelloWorld.exe (HelloWorld on Linux, not created on macOS.)
This is the framework-dependent executable version of the application. The file is operating-system-specific.
HelloWorld.pdb (optional for deployment)
This is the debug symbols file. You aren't required to deploy this file along with your application, although you should save it in the event that you need to debug the published version of your application.
HelloWorld.runtimeconfig.json
This is the application's run-time configuration file. It identifies the version of .NET that your application was built to run on. You can also add configuration options to it. For more information, see .NET run-time configuration settings.
Run the published app
In Explorer, right-click the publish folder (Ctrl-click on macOS), and select Open in Terminal.
On Windows or Linux, run the app by using the executable.
On Windows, enter
.HelloWorld.exeand press Enter.On Linux, enter
./HelloWorldand press Enter.Enter a name in response to the prompt, and press any key to exit.
On any platform, run the app by using the
dotnetcommand:Enter
dotnet HelloWorld.dlland press Enter.Enter a name in response to the prompt, and press any key to exit.
Additional resources
Next steps
Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal File
Mac Run Visual Studio Code From Terminal Command
In this tutorial, you published a console app. In the next tutorial, you create a class library.
